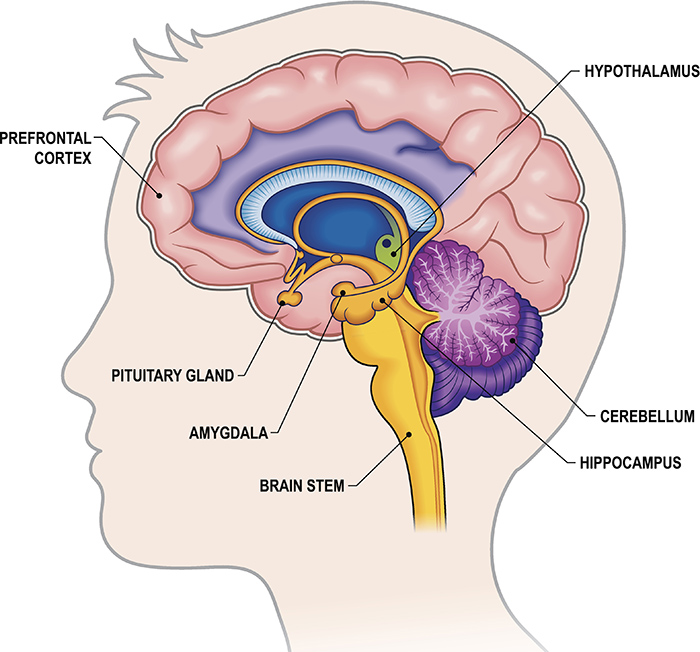
The limbic system is a set of interconnected brain structures that play a vital role in our emotions, memories, and behaviors. It is located deep within the brain, beneath the cerebral cortex (the outer layer of the brain that is responsible for higher-order cognitive functions).
The limbic system is made up of a number of different structures, including the amygdala, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and basal ganglia. Each of these structures plays a unique role in the limbic system’s overall function.
Amygdala
The amygdala is an almond-shaped structure that is responsible for processing and responding to emotions, especially fear and aggression. It also plays a role in memory formation and the fight-or-flight response.
Hippocampus
The hippocampus is a seahorse-shaped structure that is responsible for memory formation and consolidation. It is also involved in spatial navigation and learning.
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is a small structure that is responsible for regulating a wide range of bodily functions, including hormones, sleep, and appetite. It also plays a role in emotions and motivation.
Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia are a group of structures that are involved in motor control, learning, and habit formation. They also play a role in reward processing and motivation.
Functions of the Limbic System
The limbic system is involved in a wide range of functions, including:
- Emotions: The limbic system plays a central role in processing and responding to emotions. It is involved in the generation of both positive and negative emotions, such as happiness, sadness, fear, and anger.
- Memory: The limbic system is also involved in memory formation and consolidation. It helps us to remember important events and experiences, both positive and negative.
- Behavior: The limbic system plays a role in a variety of behaviors, including motivation, aggression, and sexual behavior. It is also involved in the fight-or-flight response, which is our body’s natural response to danger.
Disorders of the Limbic System
Damage to the limbic system can lead to a variety of disorders, including:
- Anxiety disorders: Anxiety disorders are characterized by excessive worry and fear. They are thought to be caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, brain chemistry, and life experiences. Damage to the limbic system may play a role in the development of anxiety disorders.
- Mood disorders: Mood disorders, such as depression and bipolar disorder, are characterized by changes in mood and energy levels. They are thought to be caused by a combination of factors, including genetics, brain chemistry, and life experiences. Damage to the limbic system may play a role in the development of mood disorders.
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD): PTSD is a mental health condition that can develop after a person experiences or witnesses a traumatic event. It is characterized by symptoms such as flashbacks, nightmares, and avoidance of situations that remind the person of the trauma. Damage to the limbic system may play a role in the development of PTSD.
Conclusion
The limbic system is a complex and important part of the brain that plays a vital role in our emotions, memories, and behaviors. Damage to the limbic system can lead to a variety of disorders, including anxiety disorders, mood disorders, and PTSD.
If you are experiencing any symptoms that may be related to a disorder of the limbic system, it is important to see a doctor or mental health professional for diagnosis and treatment.
Linda C J Turner
Emotional Trauma Therapist
http://Parentalalienationpas.com
Linda Turner, Emotional Trauma Therapist ✨
Guiding your journey from pain to power 💫
Certified Therapist | Virtual Sessions
🌱 Specialising in emotional recovery
🌟 Creating space for healing and growth
💌 DM for inquiries or visit https://linktr.ee/LindaCJTurner
